top of page

LEADING CHANGE THROUGH EVIDENCE-BASED PRACTICE

Health Promotion


Typhoid Is Far More Serious Than We Think
In Nigeria, the word "typhoid" is used almost casually. A headache? Typhoid. Fever for two days? Typhoid. Malaria symptoms that refuse to disappear after one dose of drugs? “It must be typhoid too; treat both together.” This belief has become so common that many people treat typhoid without ever confirming its presence. Unfortunately, this misunderstanding has serious consequences, because typhoid fever is not a mild illness , and it is not something that should be guessed o

Pharm. Onyehalu Jennifer
5 days ago3 min read


Five Habits Women Believe Are Healthy but Are Actually Harmful
Many women make conscious efforts to maintain good health, which is commendable. However, certain habits that are commonly perceived as harmless or beneficial can, over time, negatively affect health when misunderstood or practiced excessively.

Pharm. Onyehalu Jennifer
Jan 32 min read

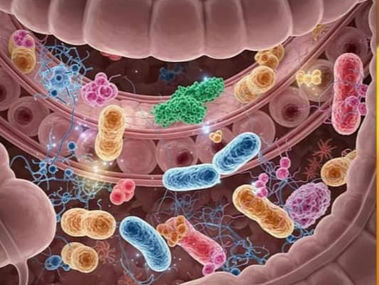
Your Gut, Your Mood: The Science Behind the Gut-Brain Connection
The gut-brain axis describes the two-way communication that occurs between our gut and brain. Signals travel through various pathways, including hormones, nerves, and immune responses.
A prime example is the vagus nerve, which transmits signals between the gut and brain. This connection enables the gut microbiome, the trillions of microorganisms living in our intestines, to affect our mood and behavior.

Pharm. Onyehalu Jennifer
Jul 7, 20253 min read


Health Education, Free Treatment, and Smiles: U-Health Medical Team Impacts Satellite Town
The residents of Satellite Town witnessed a life-changing event on April 19, 2025.

U-Health Review
Apr 29, 20253 min read



Members
Bobby Fitness Studio
Join us on mobile!
Download the “” app to easily stay updated on the go.



bottom of page